Exact solution of the perihelion motion of Mercury from Newtonian mechanics
ABSTRACT.
MATERIALS AND METHODS.
From the balance formula of centrifugal force and universal gravitational force,
GM☉ mG/r²=mI v²/r (1).
In other words, when viewed from the coordinate system, the gravity balances the inertial force, and it appears that the gravity has disappeared. It means that gravity and acceleration can be canceled out in a small area. However, in order for Eq. (1) to hold, the gravitational mass mG and the inertial mass mI must be equal. In general relativity, the motion in the gravitational field is given by the geodesic curve, and the geodesic equation does not depend on the mass. A geodesic is a metric that is not Euclidean, that is, the shortest path in space-time.
:
However, the mass equivalence (mG=mI) is a slow approximation for (v≪c), and the moving body has an exact solution of (mG≠mI).
The scale factor of the light equivalence principle that distinguishes the change in inertial mass due to scale and the change in gravitational mass due to increase or decrease in energy is
γ=mI/mG=c/w=c/√(c²±v²) (2).
Eliminating the mass of Mercury from (Equation 1) with the reference frame of the light velocity (c) of (Equation 2) point at infinity,
4 π² γ=GM☉ P²/r³ (4).
The error of one revolution revolving from the scale factor on the left side is
⊿φ=4 π²(γ-1) (5).
In arc seconds,
"x=⊿φ(180/π)*3600 (6).
By Francisco Esquembre-Author's own work, CC view-inheritance 3.0, by link.
Mercury orbits the Sun in 88 days, which means that it has rotated about 415 revolutions in 100 years, so the arc of 415 orbits is
"y=4 π(γ-1)*180*3600*415 (7).
For those who are particular about eccentricity, we have obtained (v²) from Newtonian mechanics,
v²=GM☉/r=GM☉(1-e²)/l (8),
It is a good idea to calculate by including such as.
OGPイ
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION.
The correction from the approximate solution of "Absolute rest reference system + Newtonian mechanics" by general relativity using Schwart-Schild solution and geodesic equation is not accurate.
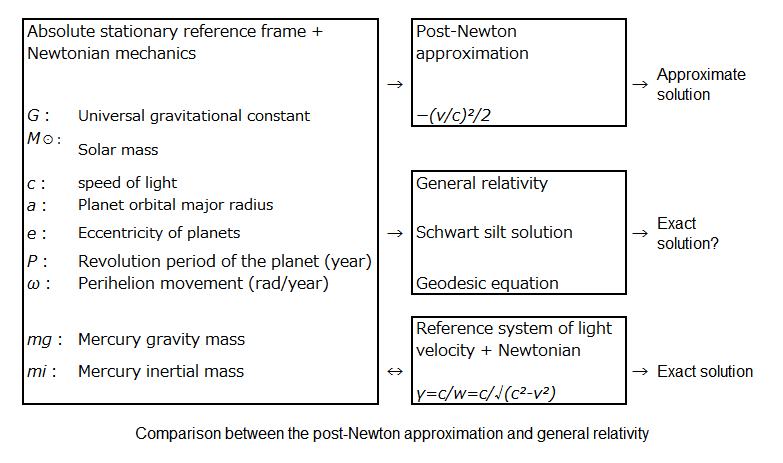
If we can be obtained the average orbital velocity (v) from them, the exact solution of the orbital motion of Mercury can be obtained from the ratio (γ) of the speed of light (c) and the average wave speed (w).

CONCLUSION.
"Light velocity (c) = wave speed (w), gravitational mass (mG) = inertial mass (mI)" only occurs at relative velocity (v = 0). This is the viewpoint seen from the local inertial system that general relativity says. However, the experience value obtained from Newtonian mechanics is another viewpoint assuming point at infinity. This approximation, which adds a second term without converting from the observer's speed of light to the wave speed of the object, causes a delta function problem at full scale of micro and macro.
In the principle of light equivalence, after converting to “light's observational reference frame”,
w²=c²±v².
Since it is dilated to the wave speed (w) of the moving object (v) seen from the observer (c) and treated as a single term, the delta function problem like general relativity does not occur.
E=c |p|=h f=mG c²=γ mI w².
Light momentum equivalence principle.
Since the mass of a body and the speed of light are closely related to the momentum of light, there are incorrect to immutable them by the classical principle of relativity.
Acknowledgment。
Thanks to everyone who parasitized on 5ch and argued, the prospect of this paper improved.
Appendix。
1. General relativity effect by relativity of atomic clock mounted on GPS satellite + special relativistic effect of post-Newton approximation,
Surface speed of light (c): 299,792,458 m/s.Geocentric gravity constant (GM): 3.986e+14 m³/s².Earth radius (r): 6,378,000 m.Hyperbolic infinite wave speed, w∞=√(c²+2GM/r).GPS satellite altitude (h): 20,200,000 m.Orbital velocity of GPS satellites (v): 3,874 m/s.Wave speed of GPS satellites, wG=√(w∞²-2GM/(r+h)-v²).Difference in how the clock progresses, wG/c=1+4.45e-10.




Comments
Post a Comment